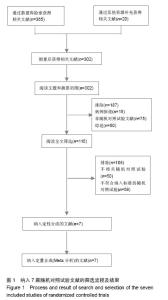
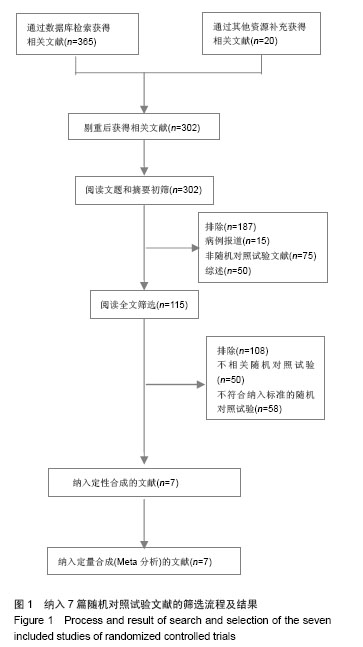
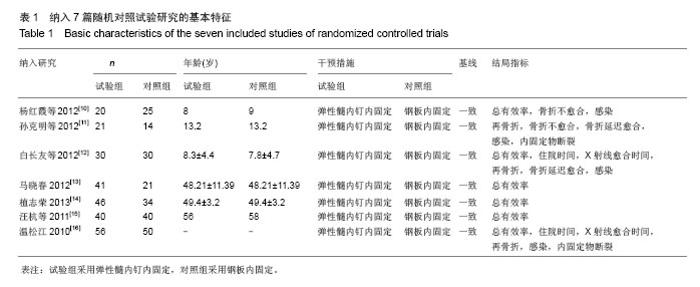
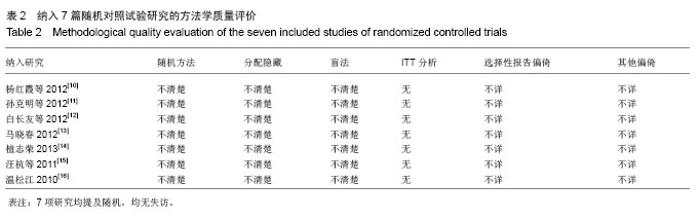
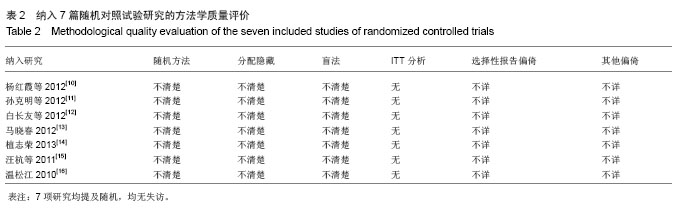
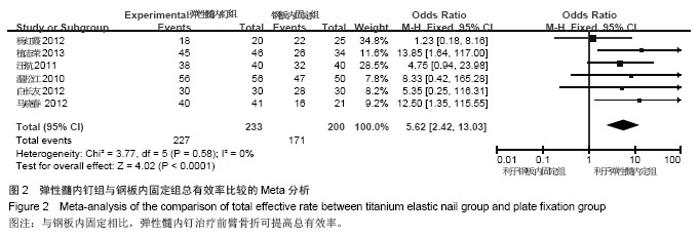
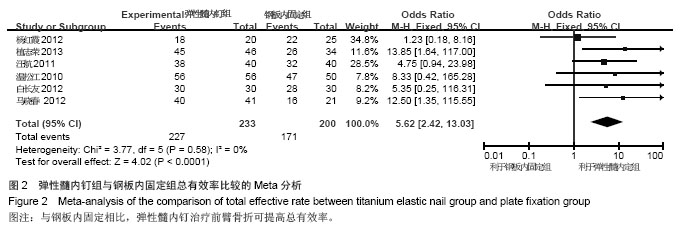
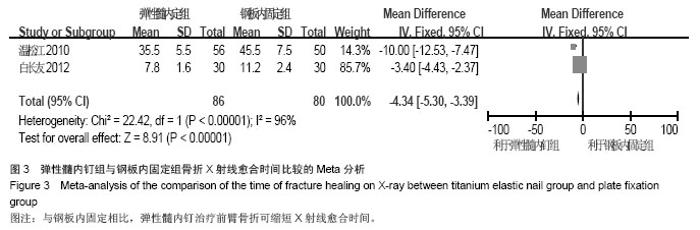
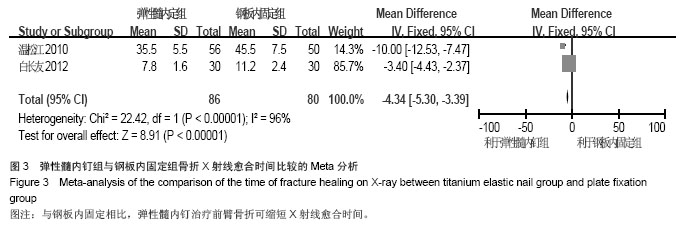
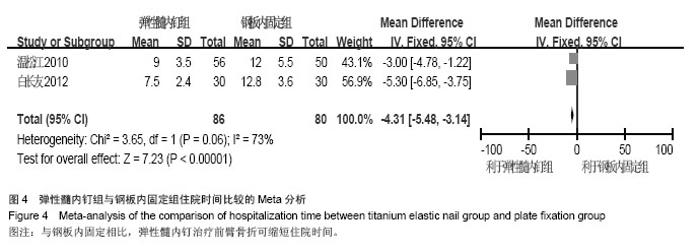
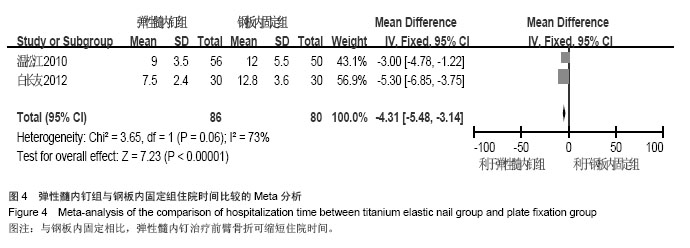
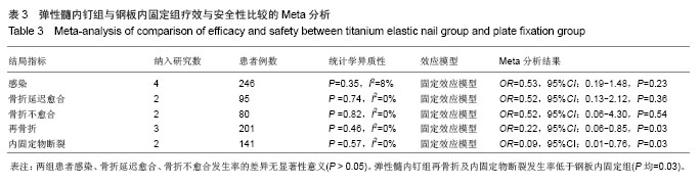
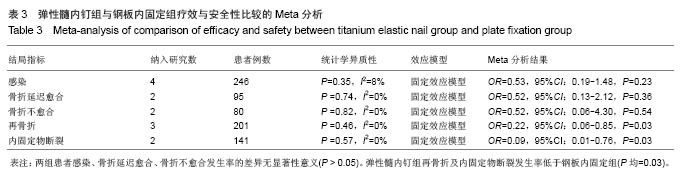
| [1] |
Chen Junming, Yue Chen, He Peilin, Zhang Juntao, Sun Moyuan, Liu Youwen.
Hip arthroplasty versus proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1452-1457.
|
| [2] |
Chen Jinping, Li Kui, Chen Qian, Guo Haoran, Zhang Yingbo, Wei Peng.
Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid in open spinal surgery
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1458-1464.
|
| [3] |
Hu Kai, Qiao Xiaohong, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong, Qin Sihe.
Treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures with cannulated screws and plates: a meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1465-1470.
|
| [4] |
Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei.
Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476.
|
| [5] |
Wang Yongsheng, Wu Yang, Li Yanchun.
Effect of acute high-intensity exercise on appetite hormones in adults: a meta-analysis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1305-1312.
|
| [6] |
Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian.
Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148.
|
| [7] |
Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei.
Intravenous, topical tranexamic acid alone or their combination in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 948-956.
|
| [8] |
Li Yan, Wang Pei, Deng Donghuan, Yan Wei, Li Lei, Jiang Hongjiang.
Electroacupuncture for pain control after total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 957-963.
|
| [9] |
He Xiangzhong, Chen Haiyun, Liu Jun, Lü Yang, Pan Jianke, Yang Wenbin, He Jingwen, Huang Junhan.
Platelet-rich plasma combined with microfracture versus microfracture in the treatment of knee cartilage lesions: a meta-analysis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 964-969.
|
| [10] |
Hua Haotian, Zhao Wenyu, Zhang Lei, Bai Wenbo, Wang Xinwei.
Meta-analysis of clinical efficacy and safety of antibiotic artificial bone in the treatment of chronic osteomyelitis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 970-976.
|
| [11] |
Zhan Fangbiao, Cheng Jun, Zou Xinsen, Long Jie, Xie Lizhong, Deng Qianrong.
Intraoperative intravenous application of tranexamic acid reduces perioperative bleeding in multilevel posterior spinal surgery: a meta-analysis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 977-984.
|
| [12] |
Zhong Yuanming, Wan Tong, Zhong Xifeng, Wu Zhuotan, He Bingkun, Wu Sixian.
Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of percutaneous curved vertebroplasty and unilateral pedicle approach percutaneous vertebroplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 456-462.
|
| [13] |
Li Yang, Zhang Mingyong.
Meta-analysis of the effect of double Endobutton and clavicular hook plate on the treatment of acromioclavicular dislocation
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 463-470.
|
| [14] |
Li Yanle, Yue Xiaohua, Wang Pei, Nie Weizhi, Zhang Junwei, Tan Yonghai, Jiang Hongjiang.
Intramedullary nail fixation versus plate fixation in the treatment of displaced midshaft clavicular fractures in adults: a meta-analysis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 471-476.
|
| [15] |
Liu Chang, Han Shufeng.
Interlocking intramedullary nail for proximal femur versus proximal femoral anti-rotation intramedullary nail or proximal femoral anti-rotation intramedullary nail of Asian for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 477-485.
|